Chlorhexidine is not an essential component in alcohol-based surgical hand preparation: a comparative study of two handrubs based on a modified EN 12791 test protocol
Background: Surgical hand preparation is an essential part of modern surgery. Both alcohol-based and antiseptic
detergent-based hand preparation are recommended practices, with a trend towards use of alcohol based
handrubs. However, discussion has arisen whether chlorhexidine is a required ingredient in highly efficacious
alcohol-based formulations, in view of providing sustained antimicrobial efficacy.
Methods: One alcohol-only formulation (product A), containing ethanol and n-propanol, and one formulation
containing a chlorhexidine-ethanol combination (product B) were directly compared with each other using a modified
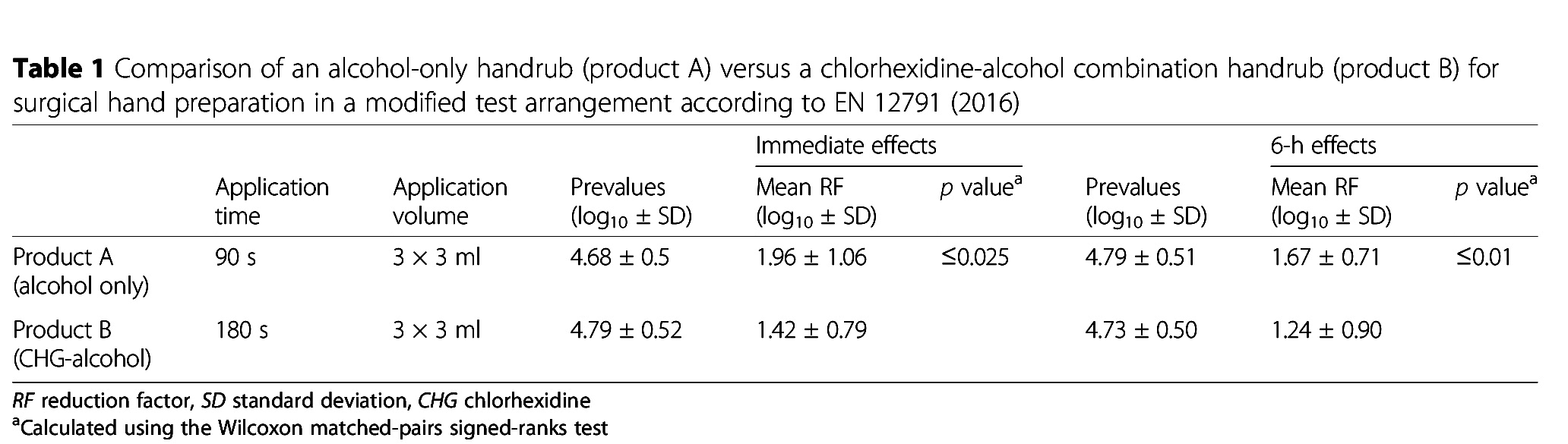
test protocol based on European standard EN 12791 (2016) with 25 volunteers. The alcohol-only formulation (product A)
was applied for only 90 s, the chlorhexidine-alcohol formulation (product B) for 180 s. Microbial log reduction factors
were determined and statistically compared immediately after application and at 6 h under surgical gloves.
Results: The alcohol-only formulation (product A) achieved mean log reduction factors of 1.96 ± ۱٫۰۶ immediately
after application and 1.67 ± ۰٫۷۱ after 6 h. The chlorhexidine-alcohol combination (product B) achieved mean log
reduction factors of 1.42 ± ۰٫۷۹ and 1.24 ± ۰٫۹۰ immediately and after 6 h, respectively. The values for product A were
significantly greater than those for product B at both measured time points (p ≤ ۰٫۰۲۵ immediately after application
and p ≤ ۰٫۰۱ after 6 h).
Conclusions: An optimized alcohol-only formulation tested according to a modified EN 12791 protocol in 25 healthy
volunteers outperformed a chlorhexidine-alcohol formulation both immediately after application and at 6 h under
surgical gloves, despite a much shorter application time. Thus, optimized alcohol-only formulations do not require
chlorhexidine to achieve potent immediate and sustained efficacy. In conclusion, chlorhexidine is not an essential
component for alcohol-based surgical hand preparation.
Refrence:
Hennig et al. Antimicrobial Resistance and Infection Control (2017) 6:96
DOI 10.1186/s13756-017-0258-0